Network
The Library—>Network
configuration page allows you to view and update the routing
information on the jetNEXUS ALB-X. The settings are organised in the
following sections:
-
Basic Setup
-
Adapter Details
-
Interfaces
-
Bonding
-
Static Route
-
Static Route details
-
Advanced Network Settings
Basic Setup
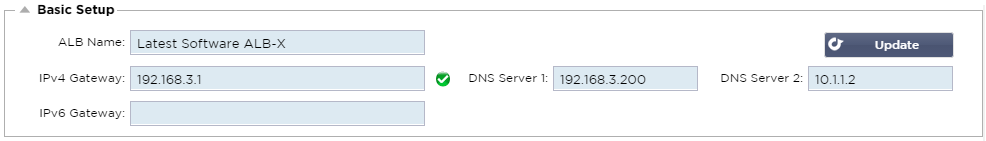
Basic Setup:
ALB Name:
jetNEXUS ALB-X appliance. Please note that this cannot be changed
if there is more than 1 member in the Cluster. Please see Clustering
IPv4 Gateway:
This will need to be in the same subnet as an existing adapter. If you
add in Gateway incorrectly you will see a White Cross in a red circle. When you add in a correct gateway you will see a green success banner at the bottom of the page and a white tick in a green circle next to the IP address.
IPv6 Gateway:
in the IPv6 Gateway address. This will need to be in the same
subnet as an existing adapter. If you add in Gateway incorrectly you
will see a White Cross in a red circle. When you add in a correct
gateway you will see a green success banner at the bottom of the page
and a white tick in a green circle next to the IP address.
DNS Server 1:
DNS Server 2:
your second DNS server
Adapter Details
Here you can add, remove and update the adapter settings.
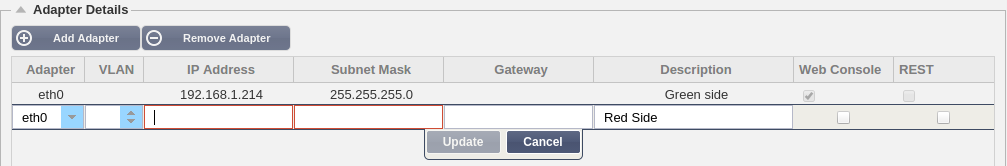
Adapter:
physical adapters installed on your appliance. Choose an adapter from the list
VLAN:
click to add the VLAN ID for the adapter. A VLAN is a Virtual Local
Area Network which creates a distinct broadcast domain. A VLAN has the
same attributes as physical LAN but it allows for end stations to be
grouped together more easily if they are not on the same network switch
IP Address:
click to add the IP address associated with the adapter
interface.
You can add multiple IP addresses to the same interface. This should be an IPv4 32-bit number in quad dotted decimal notation.
Example: 192.168.101.2
Subnet Mask:
click to add the subnet mask assigned to the adapter interface. This
should be an IPv4 32-bit number in quad dotted decimal notation.
Example: 255.255.255.0
Gateway:
this is added the ALB-X will set-up a simple policy that will allow
connections initiated from this interface to be returned via this
interface to the gateway router specified. This allows the ALB-X to be
installed in more complex networking environments without the hassle of
manually configuring complex policy based routing.
Description:
description for your adapter. Example: Public Interface. Note: The ALB-X will automatically name the first interface Green Side, the second interface Red Side and the third interface Side 3 etc. Please feel free to change these naming conventions to your own choice.
Web Console:
click the column then tick the box to assign the interface as the
management address for the Graphical User Interface Web Console.
Please be very careful when changing the interface that Web Console
will listen on. You will need to have the correct routing set up or be
in the same subnet as the new interface in order to reach the Web
Console after the change. The only way to change this back is to access
the command line and issue the set greenside command. This will delete all interfaces except for eth0.
Interfaces

- The settings on this screen control the network access. The defaults
are to fix speed at 100 Mbps and full duplex. This avoids any issue
with certain networking devices that have auto-negotiation which
re-negotiates too frequently. - The appliance can support speeds from 10 to 1000; for 1000 this should
set to auto/auto. If this does not work, set the exact network hardware
values. - The speed and duplex setting should only be changed for hardware
appliance.- Virtual appliances will take their configuration from the
underlying hypervisor.
- Virtual appliances will take their configuration from the
- In this section you can add and remove interfaces to a Bond once the bond has been configured in the section below.
Bonding
Bonding allows you to aggregate multiple ports into a single group,
effectively combining the bandwidth into a single connection. Bonding
also allows you to create multi-gigabit pipes to transport traffic
through the highest traffic areas of your network. Note: this is only
relevant for your hardware version of ALB-X. Do not use bonding for the
Virtual Appliance.
Bonding Modes
balance-rr:
active-backup:
and the second interface will be in standby. This secondary interface
only becomes active if the active connection on the first interface
fails.
balance-xor:
based on source MAC address XOR’d with destination MAC address. This selects the same slave for each destination Mac address.
broadcast:
802.3ad:
Utilizes all slaves in the active aggregator according to the 802.3ad
specification.
balance-tlb:
Incoming traffic is received by the current slave. If the receiving slave fails, another slave takes over the MAC address of the failed receiving slave.
balance-alb:
mode: also includes balance-tlb plus receive load balancing (rlb) for
IPV4 traffic, and does not require any special switch support. The
receive load balancing is achieved by ARP negotiation. The bonding
driver intercepts the ARP Replies sent by the local system on their way
out and overwrites the source hardware address with the unique hardware
address of one of the slaves in the bond, such that different peers use
different hardware addresses for the
server.
Configure Bonding
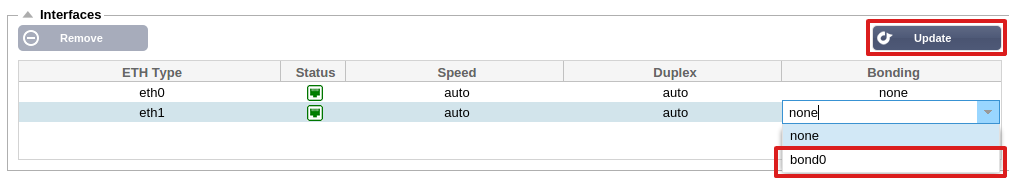
- Click on Add button on the bonding section and choose which bonding mode you wish to use
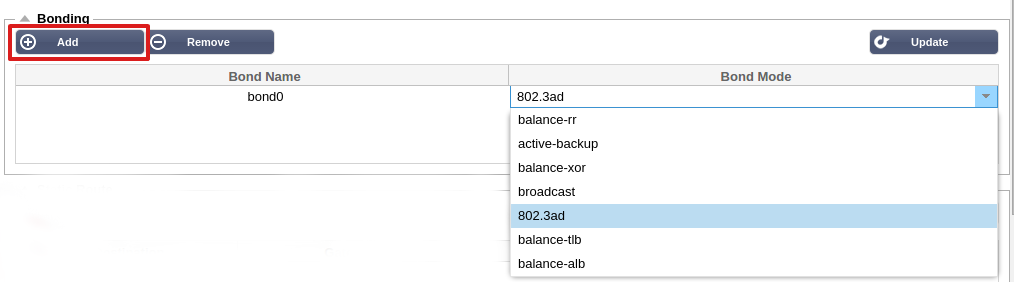
- Assign which interfaces are to be bonded in the interface
section. In the example below eth0, eth1 and eth2 are now part of
bond0. Whilst Eth0 remains on its own as the management interface
Adapter Status
![]() Adapter Up
Adapter Up
![]() Adapter Down
Adapter Down
![]() Adapter Unplugged
Adapter Unplugged
![]() Adapter missing
Adapter missing
IP Addressing
Now that you have added your bond you can go to the Adapter Details section to add the IP address and policy routing details
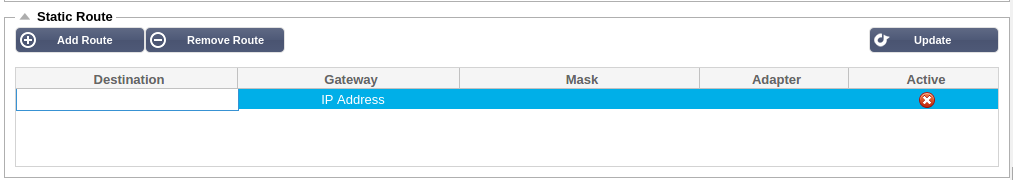
Static Route
You can manually add routes for specific subnets in this section.
Destination:
Gateway:
Mask:
Adapter:
Active:
gateway can be reached. A red cross will indicate that the gateway
cannot be reach on that interface. Please make sure you have set up an
interface and IP address on the same network as the gateway
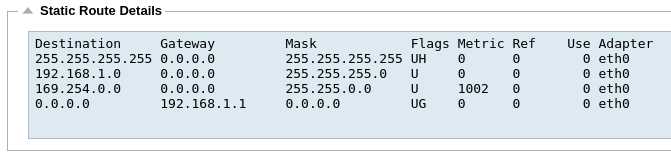
Static Route Details
This section will provide information about all of the routes configured on your ALB-X.
Advanced Network Settings
Server Nagle:
Client Nagle:
 Back to
Back to